Table of Contents
人类的作用:监督和保护
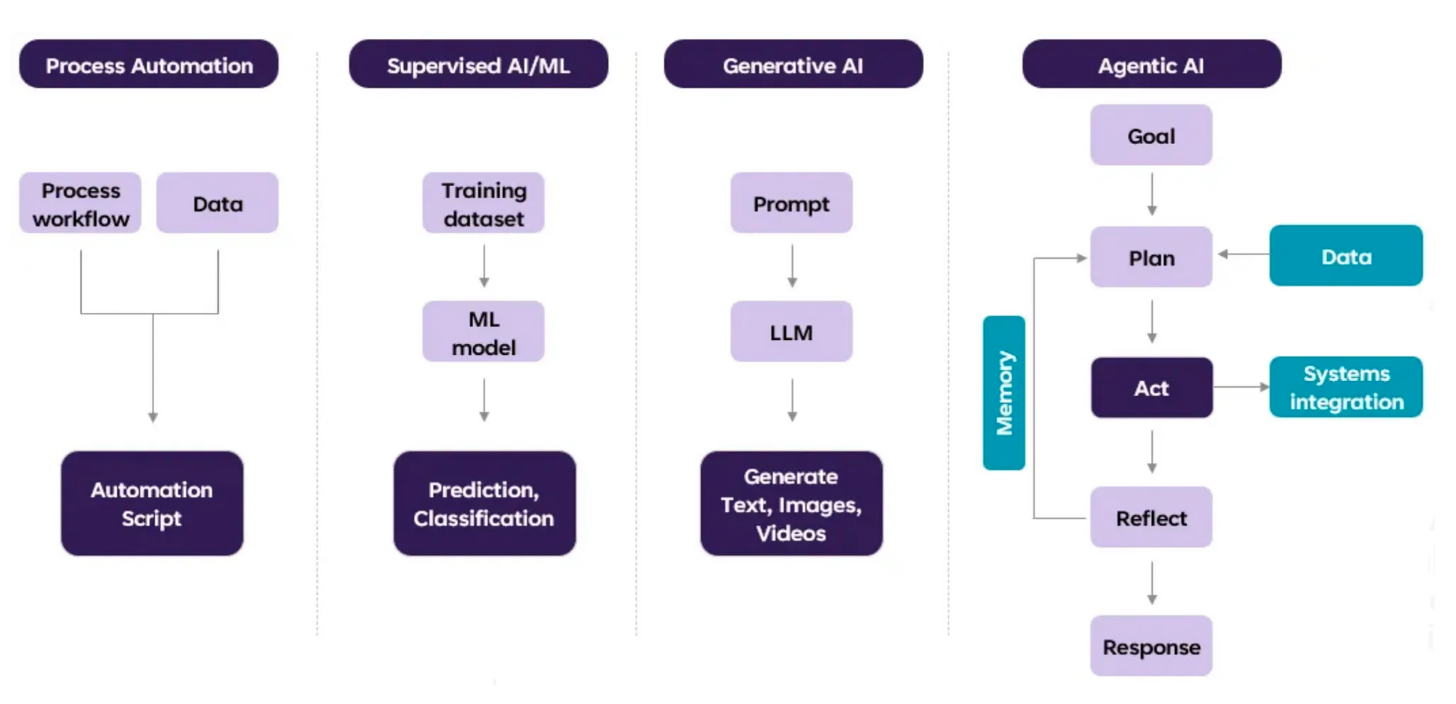
自动化的演化
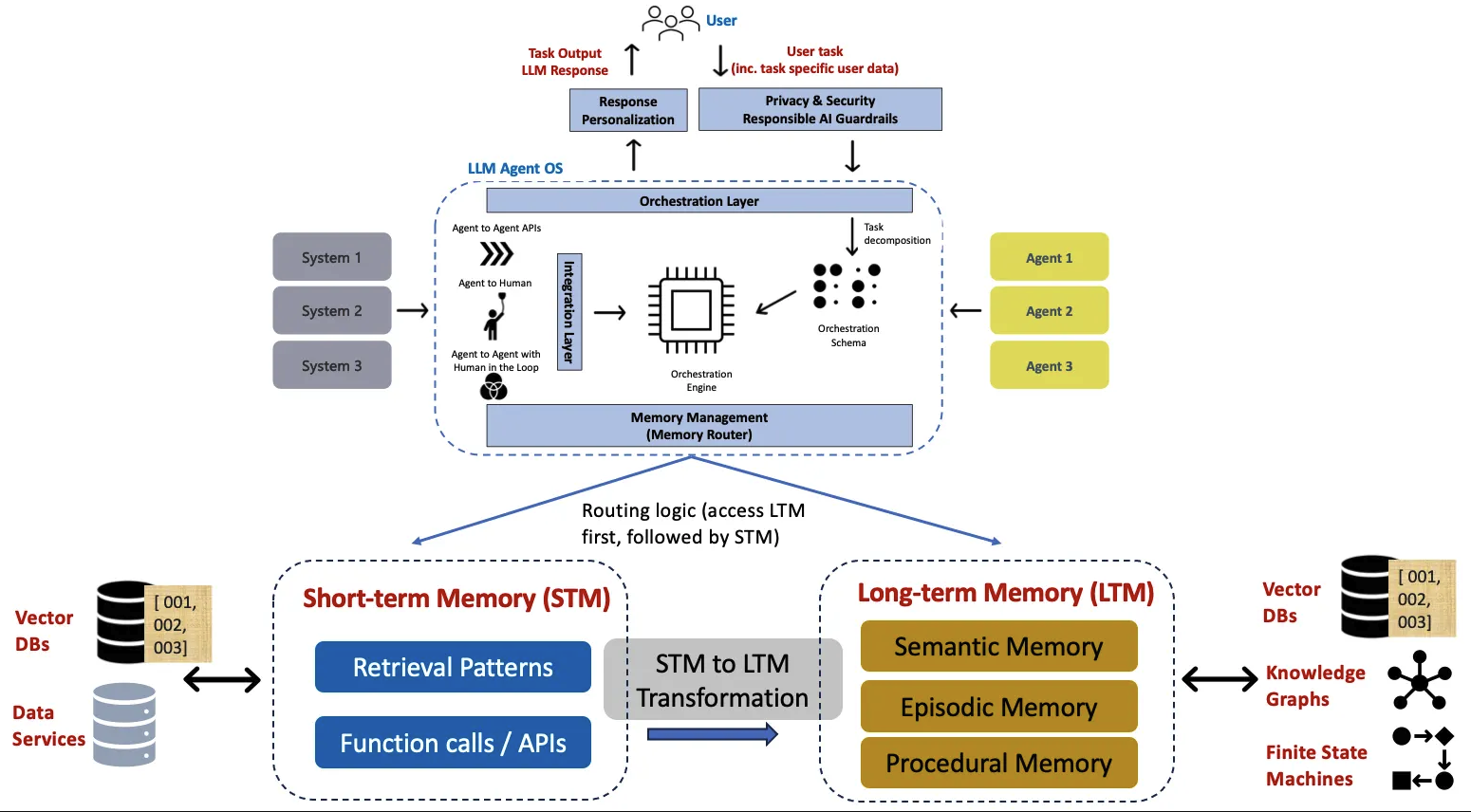
Agent开发的生命周期阶段
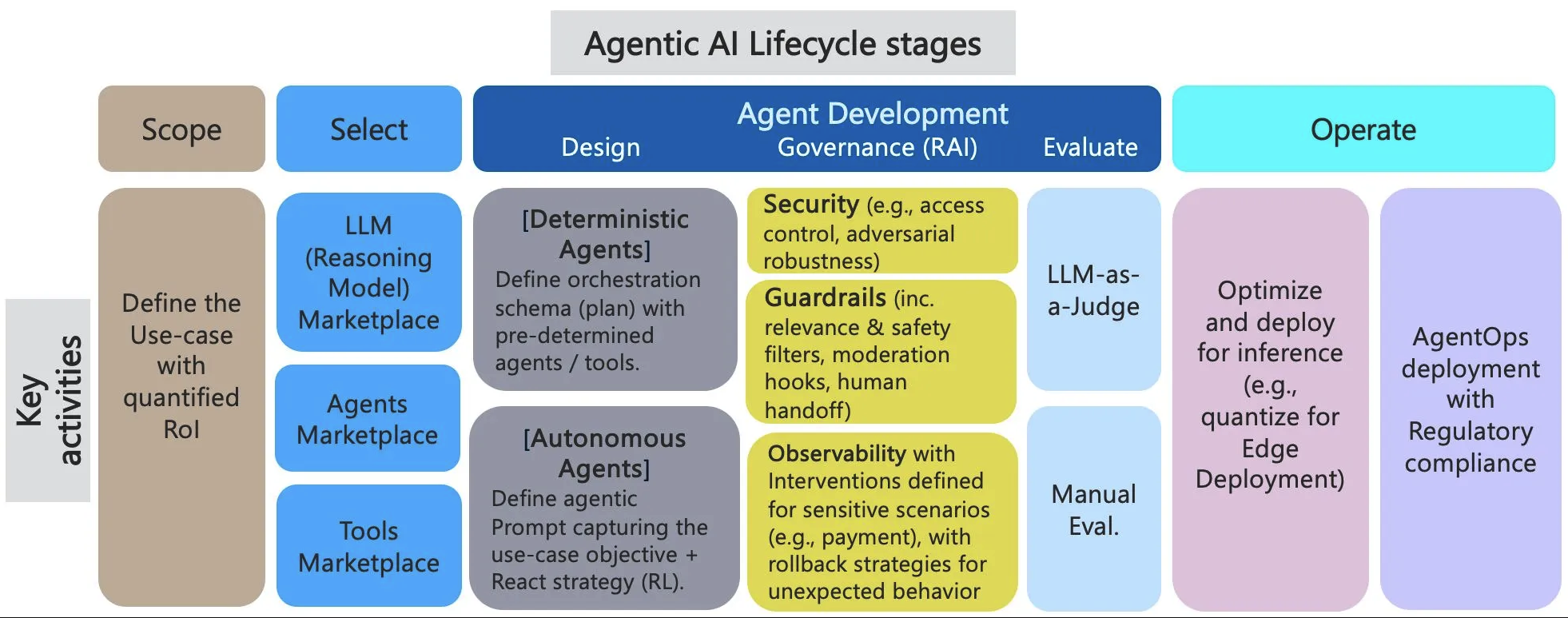
- Use-Case Definition: Clearly define the problem, business context, data requirements, and objectives (including ROI) for the agentic AI solution.
- Marketplace of Models, Agents, and Tools: Establish a repository of pre-built reasoning models (LLMs), agents, and tools with well-defined capabilities and interfaces (like Agent Cards and MCP) for easy discovery and integration. The author argues that a more formal, capabilities/constraints-based discovery model is needed for better automation.
- Agentic Logic Design: Design the agent’s execution plan, differentiating between deterministic (pre-defined orchestration) and autonomous agents (dynamic planning based on environmental observations).
- Inferencing Optimization: Optimize the deployment of agents for efficient inference, potentially including edge deployment and cost/power considerations.
- Governance Layer: Implement a robust governance layer with guardrails, end-to-end observability, and rollback strategies to ensure reliability, security, and compliance with enterprise policies. This is considered crucial for production deployment.
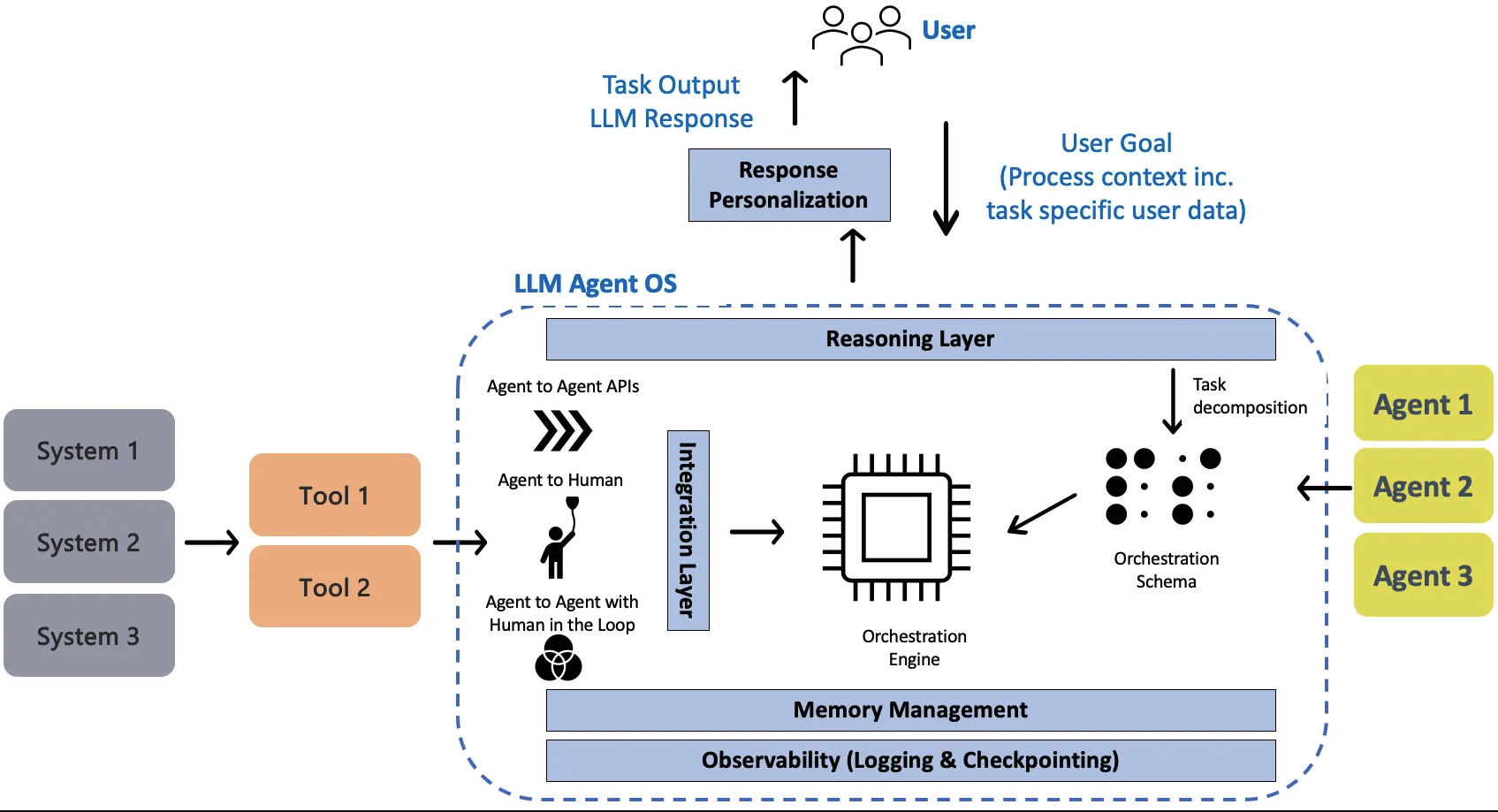
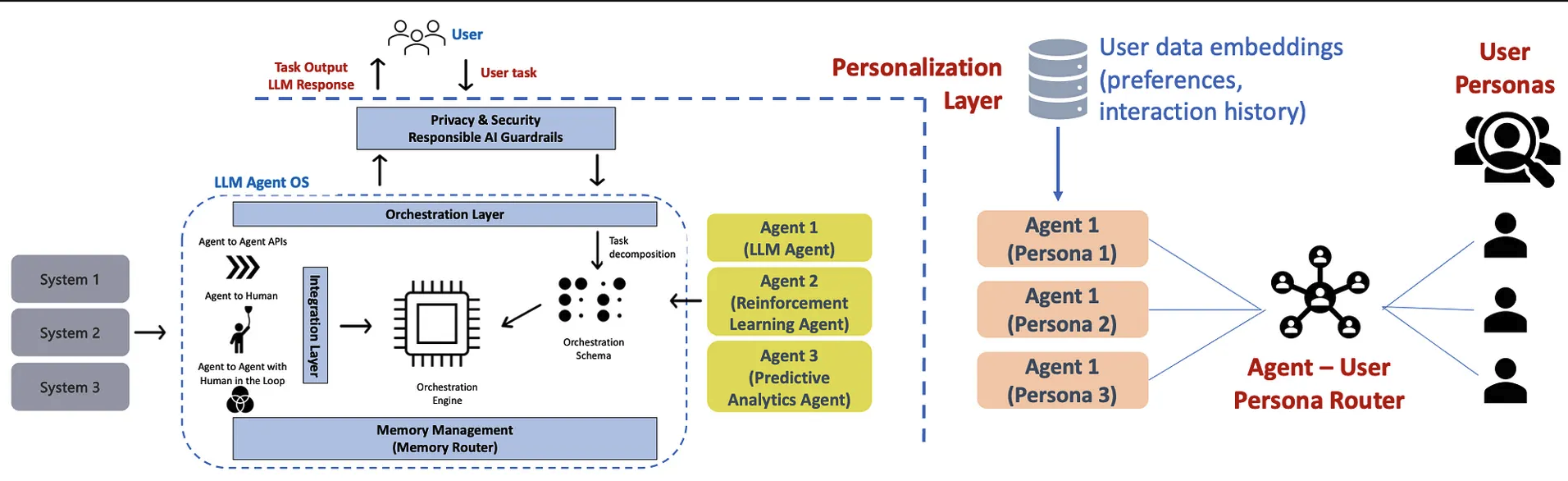
Agent自动化存在风险
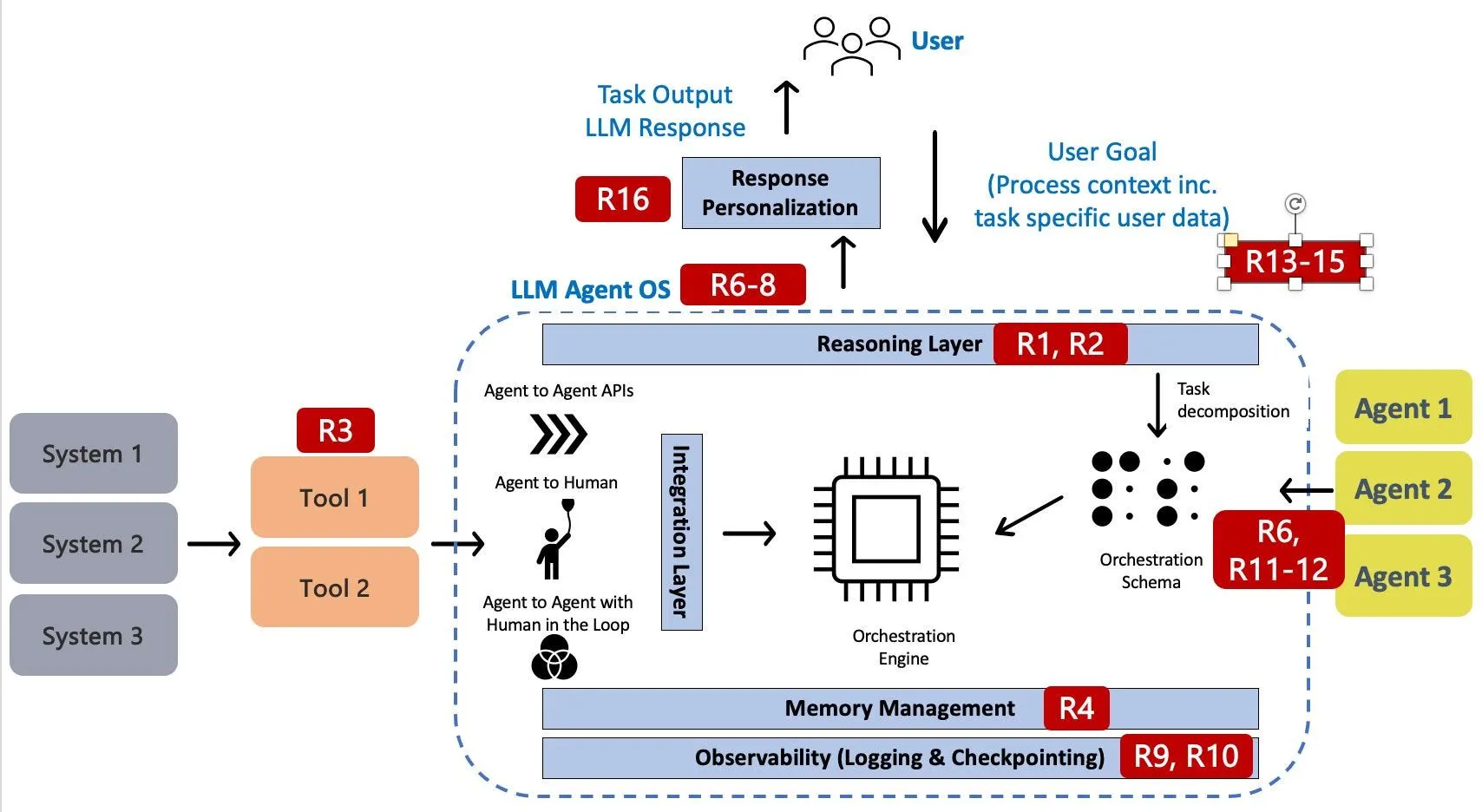
- R1: Misaligned & Deceptive Behaviors (Dynamic Deception) - 行为风险 (行为不端或欺骗性行为)
- R2: Intent Breaking & Goal Manipulation (Goal Misalignment) - 行为风险 (目标偏离或被操纵)
- R3: Tool Misuse (Tool/ API Misuse) - 工具滥用 (滥用工具或 API 接口)
- R4: Memory Poisoning (Agent Persistence) - 记忆中毒 (代理的持久化记忆受到恶意攻击)
- R5: Cascading Hallucination Attacks (Cascading System Attacks) - 级联幻觉攻击 (系统性的幻觉攻击)
- R6: Privilege Compromise - 安全漏洞 (权限泄露)
- R7: Identity Spoofing & Impersonation - 安全漏洞 (身份欺骗)
- R8: Unexpected RCE & Code Attacks - 安全漏洞 (意外的远程代码执行攻击)
- R9: Resource Overload - 运营弹性 (资源过载)
- R10: Repudiation & Untraceability - 运营弹性 (抵赖和无法追踪行为)
- R11: Rogue Agents in Multi-agent Systems - 多代理勾结 (多代理系统中的恶意代理)
- R12: Agent Communication Poisoning - 多代理勾结 (代理通信中毒)
- R13: Human Attacks on Multi-agent Systems - 多代理勾结 (人类攻击多代理系统)
- R14: Human Manipulation - 人类监督 (人类操纵)
- R15: Overwhelming Human in the Loop - 人类监督 (人机回路过载)
- R16: (Persona-driven Bias) - 人类监督 (由角色驱动的偏见)
HITL的大用
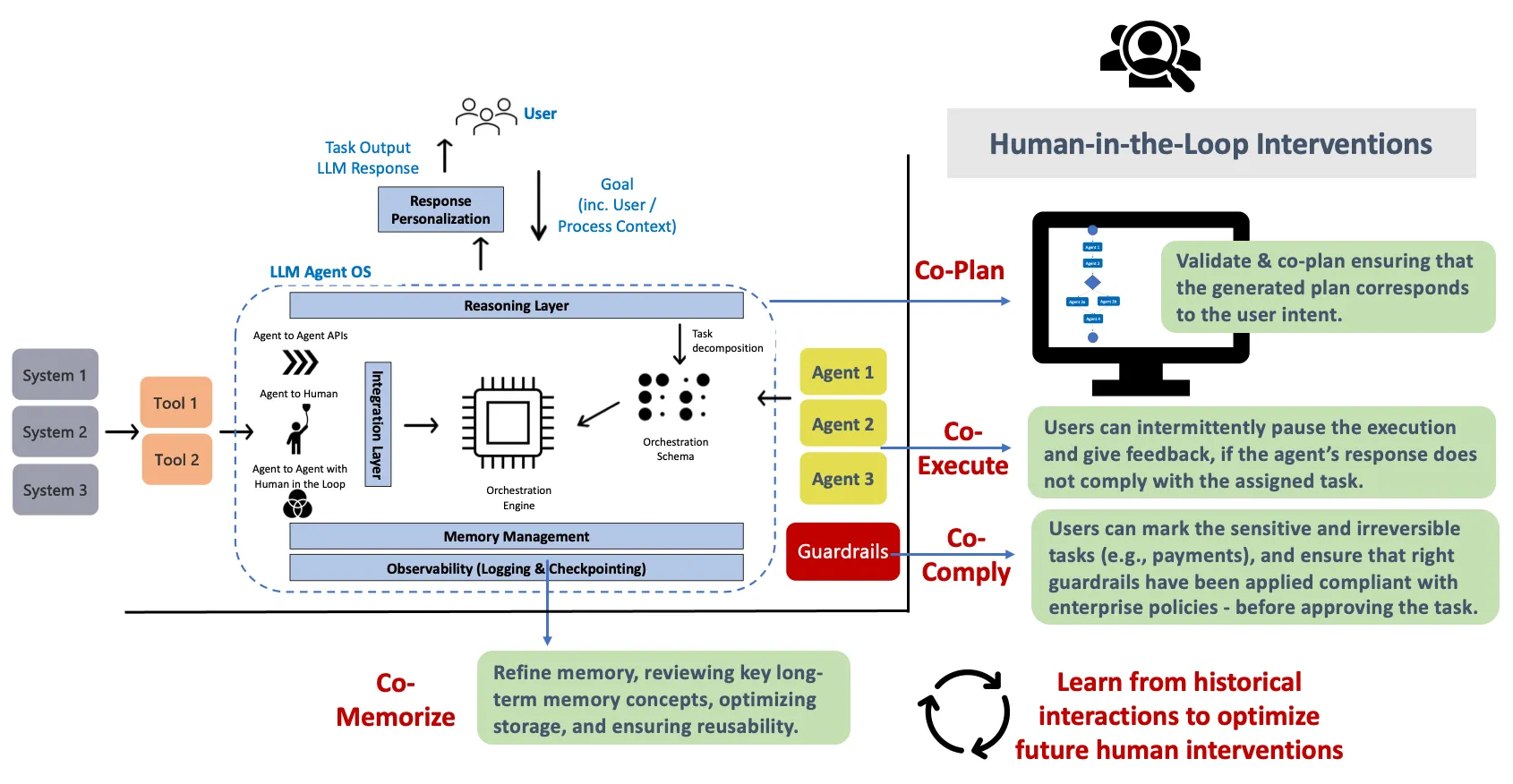
Co-plan: Validate & plan ensuring that the generated plan (orchestration graph) corresponds to the given user intent. Co-execute 就像在 AI 代理执行任务时,人类作为副驾驶员,随时监控情况,并在必要时进行干预和调整,确保任务能够成功完成。 这是一种人机协作的执行模式。 Co-comply 就像在 AI 代理执行重要操作前,让人进行一次“安全检查”,确保一切都符合规定,避免出错或造成损失。 尤其是不可逆的操作, 比如付款 Co-memorize:1. 数据可视化工具: 可以使用数据可视化工具来展示长期记忆的结构和内容,帮助人类更好地理解 AI 代理的记忆状态,并发现潜在的问题。
原文: https://ai.gopubby.com/human-in-the-loop-strategy-for-agentic-ai-d9daa22c3204


大家一起来讨论